-
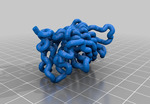
Beta Barrel
David J. Hall
Beta barrel (cyan fluorescent protein) #4AR7. This fluorescent protein is a variation of green fluorescent protein from a jellyfish and is the only domain that is a complete protein. The protein is routinely used to visualize a variety of biological processes. The beta barrel domain is a beta sheet wrapped around the fluorescent active site to provide structure.
-

CARD Domain
David J. Hall
CARD domain #1CY5. Caspase Recruitment Domains (CARDs) are modules of 90–100 amino acids involved in cell death (apoptosis) signaling pathways. CARDs mediate the association of adaptor proteins and procaspases (death proteins) through heterodimerization of their respective CARDs, recruiting procaspases to upstream signaling complexes and allowing autoactivation.
-

Death Domain
David J. Hall
Death Domain #1DDF. Death domains (DD) are 80–100 residues long motifs involved in cell death (apoptotic) signal transduction. Death domains serve as recruiting modules through their ability to heterodimerize with the death domains of distinct proteins, including adaptor proteins such as FADD.
-
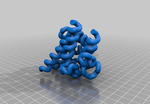
EF Hand Domain
David J. Hall
EF hand domain #2PMY. The EF-hand motif contains approximately 40 amino acids (residues) and is involved in binding intracellular calcium. Binding of calcium to regulatory EF-hand domain—containing proteins induces a conformational change, which is transmitted to their target proteins, often catalyzing enzymatic reactions.
-

Helix Turn Helix Domain
David J. Hall
Helix turn helix domain #3V1A. The helix-turn helix is a DNA-binding domain. The two alpha helices are the reading or recognition helices, which bind in a groove in the DNA and recognize specific gene regulatory sequences in the DNA.
-
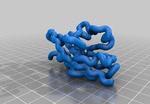
Ig Domain
David J. Hall
Ig domain #2CKN. This particular domain is named for the first protein in which it was found, the immunoglobulin. An immunoglobulin is a antibody. Antibodies are generated by our immune system to recognize the specific size, shape and charge of pathogens. This domain is also found on the extracellular portion of many receptors including the interleukin-1 family of receptors.
-

Ring Domain
David J. Hall
Ring domain #1CHC. The RING finger is a specialized type of Zn finger consisting of 40–60 residues that binds two atoms of zinc, and is involved in mediating protein—protein interactions. Many zinc fingers bind nucleic acids. The presence of a RING finger domain is a characteristic of RING-class E3 ubiquitin protein ligases capable of transferring ubiquitin from an E2 enzyme to a substrate protein.
-
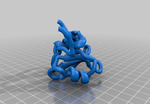
SH2 Domain
David J. Hall
SH2 domain #1BFJ. Src-homology 2 (SH2) domains are modules of ~100 amino acids that bind to specific phospho tyrosine (pY) containing peptide motifs. Conventional SH2 domains have a conserved pocket that recognizes pY, and a more variable pocket that binds 3-6 residues C-terminal to the pY and confers specificity.
-
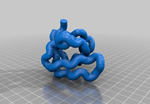
SH3 Domain
David J. Hall
SH3 domain #1NEB. Src-homology 3 (SH3) domains bind to Pro-rich peptides that form a left-handed poly-Pro type II helix, with the minimal consensus Pro-X-X-Pro. Each Pro is usually preceeded by an aliphatic residue. Each in the aliphatic-Pro pair binds to a hydrophobic pocket on the SH3 domain.
-

WW Domain
David J. Hall
WW domain #1EOM. WW domains are small 38 to 40 amino acid residue modules that have been implicated in binding to Pro-rich sequences.
Proteins are polymers of amino acids. The primary sequence of amino acids conveys to the protein the ability to fold into particular structures in three-dimensional space. Thus a protein is a series of 3D domains strung together to give a protein a particular set of functions. This collection contains downloadable protein domains and instructions.
Printing is not supported at the primary Gallery Thumbnail page. Please first navigate to a specific Image before printing.

